What is a Car Starter? What Does a Starter Do?
Definition: A car starter is a device that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy.
So, you know how a car needs to start its engine before you can drive it? Well, a car starter is a magical device that helps make that happen. It’s like a little electric motor that gives the engine a friendly push to get it going.
When you want to start your car, you turn the key or push a button, right? That sends a signal to the starter motor, telling it to do its job. The starter motor is connected to the engine and has a special gear that fits into another gear in the engine called the flywheel.
When the starter motor receives the signal, it starts spinning really fast. As it spins, its gear meshes with the flywheel gear, and this turns the engine’s crankshaft. The crankshaft is like the heart of the engine, and when it starts moving, it helps the other parts of the engine start working too.
Once the engine comes to life and starts running on its own, the starter motor stops spinning. It’s kind of like a superhero that swoops in, does its job, and then goes back to its secret lair until it’s needed again.
The starter motor needs electricity to work, and it gets that power from the car’s battery. When you turn the key or push the button, it sends an electric current from the battery to the starter motor, and that’s what makes it spin.
So, next time you start your car and hear that little whirring sound, you’ll know it’s the car starter doing its magic, getting the engine ready for your exciting adventures on the road.
Key Points Covered in the Article
- A car starter is a device that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy to start the car’s engine.
- When you turn the key or press a button to start the car, it sends a signal to the starter motor, which spins and meshes with the engine’s flywheel, turning the engine’s crankshaft and starting the engine.
- The starter motor gets its power from the car’s battery and stops spinning once the engine is running.
- The car starter system includes components such as the armature, commutator, brushes, solenoid, plunger, lever fork, pinion, and field coils, each with its own function.
- The starter system works in conjunction with the ignition system, transmission range switch (neutral safety switch), and other components to ensure safe and proper engine starting.
- Starters have limitations, and continuous cranking can cause overheating, so they are equipped with a timer that limits their operation time.
- Common problems with the starting system can include battery issues, starter motor problems, ignition switch failure, and transmission range switch issues.
- Testing the starting system involves checking the battery, battery terminals, and cables, as well as measuring voltage at the starter solenoid control terminal and ensuring a secure connection.
- If the starter motor is faulty, it will need to be replaced, and options include a new OEM part, aftermarket part, or refurbished/remanufactured part. The replacement cost can vary depending on factors such as complexity and the price of the new part.
Let Us Get Inside The Car Starter
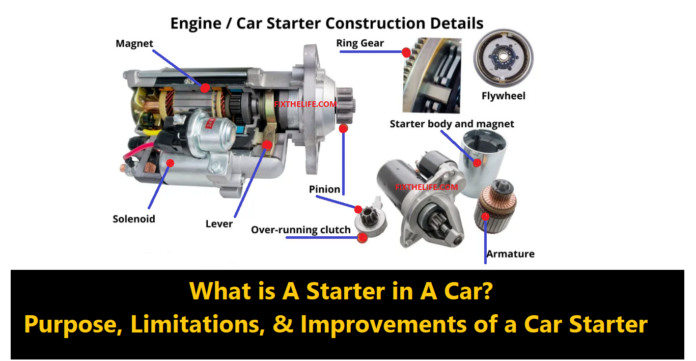
The starter pinion gear is an important part of the starter system in a car. It is connected to a component called the armature, which is like the heart of the starter.
Inside the armature, there are coils of wire wrapped around a core made of layered metal pieces. This core is often called metal lamination.
When you turn the key or push the start button in your car, an electric voltage is sent to the starter. This voltage is directed to the field brushes, which then pass it on to the commutator segments on the armature.
The coils of wire in the armature create a magnetic field when this voltage is applied.
Surrounding the armature are pole pieces, which are pieces of metal that play a crucial role in the starter’s operation.
When the electrical charge reaches the field coils, these pole pieces become powerful magnets. They have alternating north and south poles, just like the magnets you may have played with.
Now comes the fascinating part. The interaction between the magnetic forces generated by the armature and those produced by the pole pieces sets the armature in motion.
The armature starts spinning rapidly due to the strong magnetic attraction and repulsion.
The spinning motion of the armature is quite powerful. It connects to the engine’s crankshaft, which is responsible for the engine’s movement.
When the armature spins, it transfers this rotational force to the crankshaft. This action causes the crankshaft to turn, and as a result, the engine starts coming to life.
It’s important to note that this explanation provides a simplified understanding of how the starter works.
In reality, there are many more intricate details and components involved, but I hope this explanation gives you a clearer picture of the starter’s internal workings.
Car Starter Motor Components & Their Functions:
Armature:
The armature plays a crucial role in the starter motor. It is securely mounted on the drive shaft and supported by bearings to ensure stability.
Made of laminated soft iron, the armature is designed with numerous conductor loops or windings that wrap around its core. When electricity flows through these windings, the armature becomes an electromagnet.
Commutator:
Positioned at the rear of the starter motor’s housing, the commutator serves as an essential part of the motor’s shaft. It acts as a contact point for the brushes, which are responsible for conducting electricity.
The commutator consists of two plates that are firmly attached to the axle of the armature. These plates establish the necessary connections for the electromagnet coil.
Brushes:
The brushes are in direct contact with a specific section of the commutator located at the rear of the starter motor’s housing.
Their purpose is to establish a continuous electrical connection by making contact with the commutator plates. Through this contact, the brushes facilitate the transmission of electricity.
Solenoid:

The solenoid is a critical component within the starter motor. It consists of two wire coils that are wound around a movable core.
Acting as a switch, the solenoid enables the completion of the electrical connection between the starter motor and the vehicle’s battery. By engaging the solenoid, the starter motor becomes connected to the power source.
Plunger:
Driven by the power from the vehicle’s battery and the solenoid, the plunger performs a pivotal role in the starter motor’s operation.
Its primary function is to move forward, propelled by the force exerted by the solenoid. This forward motion of the plunger is responsible for engaging the pinion gear.
Lever Fork:
Intimately connected to the plunger, the lever fork moves in tandem with the plunger’s forward motion. This synchronized movement allows for the activation of the pinion gear, facilitating the transfer of power.
Pinion:
The pinion gear represents a distinctive combination of gears and springs within the starter motor.
Once the starter motor is engaged, the pinion gear extends into the gearbox housing and meshes with the flywheel. This engagement enables the rotation of the engine, initiating the combustion process.
Field Coils:
The housing of the starter motor securely holds the field coils in place, utilizing screws for stability. The number of field coils may vary, typically ranging from two to four, and they are interconnected in series.
When the battery supplies power, these field coils transform into electromagnets, generating a magnetic field. This magnetic field induces the rotation of the armature.
Through the energized armature coils, a magnetic field is formed, surrounding the armature and contributing to the starter motor’s functionality.
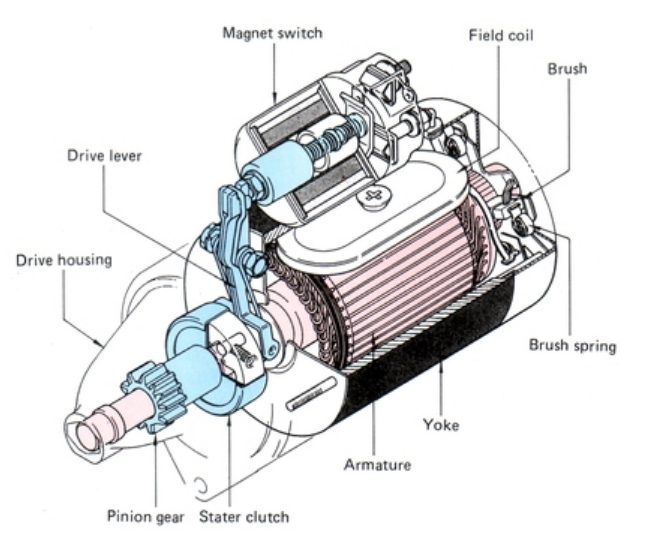
Please note that the information provided represents a general understanding of starter motor components and their functions. Variations in design and additional details may exist in specific starter motor models used in different vehicles.
How a Car Starter Design Changed Over the Years
While the basic principles of the starter motor have remained consistent since its inception, significant advancements in starter design have taken place over the years.
One notable change is the use of permanent magnets instead of pole pieces in most modern starters. In the past, electricity passing through the field coils would transform the pole pieces into powerful magnets.
However, with the introduction of permanent magnets, the starter has become more efficient as it no longer requires energy from the battery to magnetize the poles. This improvement allows for reduced power consumption.
Another significant development is the shift from direct drive designs to gear reduction drive designs in modern starters. The example image provided showcases an offset gear reduction design. This design offers several advantages.
Firstly, it allows for smaller and lighter starters to generate the same amount of torque as their direct drive predecessors. Additionally, gear reduction starters consume less energy from the battery.
It’s important to note that in this design, the pinion gear is no longer connected to the armature shaft. Instead, the armature spins at a much faster rate than the pinion gear.
In contrast, direct drive starters had the pinion gear rotating at the same speed as the armature.
These advancements in starter design, such as the utilization of permanent magnets and gear reduction drives, have significantly enhanced the efficiency and performance of starters.
By reducing power consumption and maximizing torque output, modern starters contribute to more reliable and effective starting systems in vehicles.
It’s worth mentioning that while the provided information highlights important changes in starter design, variations and further innovations may exist in specific starter models used in different vehicles.
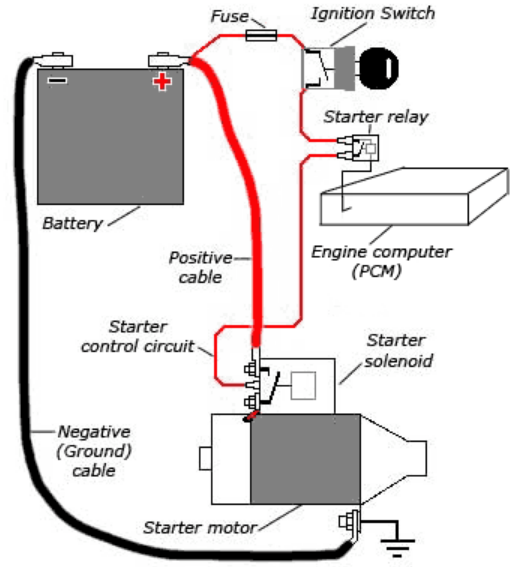
How The Starting System Works
- When you turn the ignition key to the ON position, the engine computer (PCM) checks if the ignition key security code matches the immobilizer system.
- If the security code matches, the engine is authorized to start.
- When you turn the key to the START position or press the START button, the PCM performs additional checks: It verifies if the transmission is in Park or Neutral (for automatic transmissions) or if the clutch pedal is depressed (for manual transmissions).
- It checks if the brake pedal (for automatic transmissions) or the clutch pedal (for manual transmissions) is engaged.
- It confirms if the steering lock is unlocked (in some vehicles).
- If all the checks pass successfully, the PCM activates the starter relay.
- The starter relay closes the starter control circuit, which triggers the starter solenoid.
- The starter solenoid closes the high-current circuit, allowing power to be sent to the starter motor.
- At the same time, the starter solenoid moves the starter gear forward, engaging it with the engine’s flexplate gear (or flywheel gear in manual transmissions).
- The flexplate (or flywheel) is connected to the engine’s crankshaft.
- As a result, the starter motor spins the engine’s crankshaft at a sufficient speed to initiate the engine startup process.
- In vehicles with a push-button start, the starter motor disengages as soon as the engine starts running.
Please note that specific details and terminology may vary depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and design.
What is a Neutral Safety Switch?

- To ensure safety, the starter motor is designed to operate only when an automatic transmission is in either the Park or Neutral position. In vehicles with a manual transmission, the engine can only be started when the clutch pedal is fully depressed.
- In cars equipped with an automatic transmission, a component called the transmission range switch acts as a neutral safety switch. It sends a signal to the engine computer (PCM) to indicate whether the transmission is in Park or Neutral.
- Conversely, in vehicles with a manual transmission, a clutch pedal switch serves a similar purpose. It communicates to the engine computer whether the clutch pedal is pressed down, allowing the engine to start.
- The transmission range switch plays a vital role in informing the vehicle’s computer (PCM) about the current gear selected by the transmission.
- In some cars, you may notice a gear indicator on the dashboard, which can help identify any issues with the transmission range switch.
- A common problem occurs when you shift the transmission into the Park position, but the letter “P” fails to appear on the dashboard. This indicates that the vehicle’s computer (PCM) is unaware that the transmission is in Park, resulting in the starter being disabled.
Please note that specific details and terminology may vary depending on the make, model, and configuration of the vehicle.
What is The Purpose of a Car Starter?
A starter is a special component in a car that has a specific job: to spin the engine until it can run on its own. It’s like giving the engine a helping hand to get it started.
Once the engine is running smoothly, the starter’s work is done, and it disconnects from the flywheel. It’s like the starter saying, “Okay, engine, you’re good to go now.”
Limitations of a Starter
Starters have a limited period of time they can run before they start to overheat. When you use the starter to crank the engine, it converts the energy from the car’s battery into a lot of powerful mechanical motion.
This process generates a significant amount of heat within the starter very quickly. Unlike alternators, starters don’t have a cooling mechanism, which means they rely on natural cooling methods.
If you keep cranking the engine for more than a few seconds continuously, the high temperatures can cause damage to the starter’s components.
To prevent this, many modern vehicles are equipped with a safety feature in the starting system.
This feature includes a timer that limits the time the starter can be engaged to around 10 seconds at a time. Once the time limit is reached, the starter disengages automatically.
This timer is essential in protecting the starter from overheating and prolonging its lifespan.
It ensures that the starter has time to cool down before it is used again. Allowing the starter to rest and cool helps prevent any potential damage caused by excessive heat.
So, it’s important to keep in mind the operating limitations of starters and avoid extended periods of continuous cranking.
This not only safeguards the starter but also ensures the overall health and durability of the starting system in your vehicle.
Problems With the Starting System
The starting system in a vehicle can encounter various problems, and not all of them are related to a faulty starter motor. To identify the root cause, it is important to conduct a comprehensive examination of the starting system.
If you attempt to start the car and hear the starter cranking as usual, but the engine fails to start, it indicates that the problem lies elsewhere.
For more detailed information, you can refer to the article titled “The engine cranks but won’t start.”
Let’s take a look at some common issues that can occur in the starting system:
Battery Issues:
Corroded battery terminals or poor connections can hinder the performance of the starter. Starter problems can arise when the battery terminals or ground cable connections become corroded. Cleaning these parts or replacing them, if necessary, can resolve the issue.
The battery itself can fail due to various factors, such as leaving electrical components on or experiencing a parasitic current draw. Sometimes, an old battery can suddenly lose its charge.
If the battery is low on charge, it may not provide enough power for the starter motor to turn over the engine.
Signs of a low battery charge include hearing a single click or repeated clicking sounds when attempting to start the engine. Additionally, the starter motor may rotate slowly and eventually stop.
Starter Motor Problems:
The starter motor can experience internal component wear, including worn-out carbon brushes, which can affect its operation.
In certain vehicle models like Toyota Corolla and Matrix models, a common issue is a starter motor that clicks but fails to turn over the engine.
The improper meshing of the starter gear with the engine flywheel can result in a noticeable grinding or screeching sound during startup. If this occurs, it is important to inspect the flywheel ring gear for any damaged teeth.
Ignition Switch Failure:
Ignition switch failure often occurs due to worn-out contact points within the switch.
When you turn the ignition switch to the “Start” position, it may fail to activate the starter solenoid by allowing electric current to flow through the starter control circuit.
If jiggling the key in the ignition helps start the car, it suggests a defective ignition switch.
Transmission Range Switch Issues:
The transmission range switch, also known as the neutral safety switch, can malfunction or require adjustment. For example, if your car starts in “Neutral” but not in “Park,” it is recommended to check the neutral safety switch as a potential cause.
Keep in mind that these examples represent common starting system problems, and the specific issues can vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle. It is advisable to consult with a professional mechanic for an accurate diagnosis and resolution of any starting system issues you may encounter.
ALSO READ: How to Jump Start an Engine?
How to Test The Starting System
If the starter motor is not functioning, the first thing to check is the condition of the battery, battery terminals, and battery cables. A weak or discharged battery can often be identified by dimming dashboard lights when you turn the key to the START position.
The next step is to test the starter control circuit. A professional mechanic may begin by measuring the voltage at the starter solenoid control terminal while you turn the key to START.
If there is no voltage present, the problem likely lies within the starter control circuit, which includes components such as the ignition switch, starter relay, neutral safety switch, and control wire.
However, if there is a voltage at the starter solenoid control terminal, but the starter motor still fails to engage, the issue is likely with the starter motor itself.
It is also important to ensure that the connection at the starter solenoid control terminal is secure and free from any corrosion or damage.
Please keep in mind that these are general troubleshooting steps, and the specific procedures may vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle. For an accurate diagnosis and resolution of any starter motor issues, it is recommended to consult with a qualified mechanic or technician. They will have the expertise and proper tools to diagnose and repair the problem effectively.
Repairing Options for The Car Starter Motor
If the starter motor is found to be faulty, it will require replacement, and the cost of the replacement can vary depending on factors such as the complexity of the repair and the price of the new part.
The ease of replacing a starter motor can differ between car models.
While some vehicles may allow for a straightforward replacement process, others may necessitate the removal of additional components, such as the intake manifold, to gain access to the starter motor. When considering options for replacement, there are several choices available:
- New OEM part: This option is typically the most expensive but ensures a proper fit and reliable quality since it is sourced directly from the original equipment manufacturer.
- New aftermarket part: Aftermarket starter motors are generally more affordable, but it is important to note that the quality may vary. It is advisable to select a part from a reputable brand known for producing reliable components, preferably with warranty coverage.
- Remanufactured part: Remanufactured starter motors are often priced lower than new ones, but their quality can be inconsistent. It is recommended to inquire about the available warranty and carefully consider the reputation of the supplier.
- Used part: Opting for a used starter motor is usually the least expensive option. However, it is essential to assess the condition and longevity of the used part. Inquiring about any available warranty and obtaining it from a reliable source, such as a reputable auto-recycling facility, can help mitigate potential risks.
- Rebuilding the existing starter motor: In situations where a replacement starter motor is not readily available, reaching out to a local starter/alternator shop or an auto electric shop may provide the possibility of rebuilding the existing starter motor.
Alternatively, online resources such as repair kits and instructional videos can be explored, although it should be noted that rebuilding a starter motor requires technical expertise and attention to detail to ensure proper functionality.
When making a decision about the replacement starter motor, it is crucial to carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each option, considering factors such as budget and specific requirements. Seeking guidance from a qualified mechanic or technician can provide valuable insights and assistance in selecting the most suitable option for your vehicle.
FAQs
How much does starter cost to replace?
The price range for a brand-new starter is typically between $50 and $350. When it comes to labor costs, a qualified mechanic may charge anywhere from $150 to $1,100.
Overall, replacing a faulty starter motor can result in expenses ranging from $200 to $1,450. However, if you are able to identify car starter issues early, these costs can potentially be lower.
How much does a car starter cost?
The cost of a brand-new car starter can vary significantly, typically ranging from $80 to over $350. If you opt to have a qualified mechanic handle the replacement or rebuild of your starter, you should expect to pay between $150 and over $1,100.
However, it’s important to note that these estimates can fluctuate considerably based on the specific problem with the starter as well as the make, model, and year of your vehicle.
Can you drive with a bad starter?
If you’re able to successfully start your vehicle, it’s highly unlikely that your engine will suddenly die or stall while you’re driving. However, it’s important to acknowledge that there can always be exceptions to this rule.
In some cases, a faulty starter can result in a continuous drain on the battery, preventing your vehicle from operating properly due to inadequate voltage. It’s crucial to ensure that your vehicle’s electrical components are in good working order to avoid any unexpected issues on the road.
What happens if I don’t replace the starter?
The starter motor in your car plays a crucial role by using power from the battery to kick-start the engine. However, it relies on a component called the starter relay, which acts as a power transmitter between the battery and the motor.
Without a functional starter relay and motor, your vehicle won’t be able to start, leaving you in a situation where you might require a tow.
When should a starter be replaced?
The lifespan of a starter motor can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle. On average, you can expect a factory-installed starter to last for about 100,000 miles.
However, it’s worth noting that once your vehicle’s odometer reaches this significant milestone, there is a chance that the starter may start experiencing issues.
Recommendation
How to Tell if a Fuse is Blown?
How to Test a Fuse With a Multimeter?
The Ultimate Guide to Use Power Waxer